Google Analytics is Now GA4

Google Analytics is Now GA4
As a multi-location marketer, you likely understand the importance of analytics and ensuring you have accurate data. Understanding how your current efforts are performing across local search and social channels is critical. Google Analytics often plays a significant role in measuring the success of local search efforts.
If you’re unfamiliar, Google Analytics is an analytics software offered by Google that allows users to track and report on website traffic. Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the latest version of Google Analytics. Within this article, we’ll break down what GA4 is, explain how it works, and share how your brand can leverage it to track website performance.
Let’s get into it!
Exploring GA4
On July 1, 2023, Google’s Universal Analytics stopped processing data. This move effectively forced users over to Google Analytics 4 (GA4). It’s worth noting that while Universal Analytics (UA) isn’t processing data anymore, users will still be able to access its historical data for at least another six months. So why the switch?
Google explains that it created GA4 to help businesses:
- Understand customers across touchpoints and get a complete view of the customer lifecycle.
- Improve ROI with data-driven attribution and understand how your business’s marketing efforts collectively impact conversions.
- Measure engagement and conversions with business and compliance needs in mind.
- Get more value from the data through machine learning that generates predictive insights.
- Address enterprise measurement needs with the ability to customize the structure of your business’s GA4 properties.
Now that you understand what GA4 is, let’s get into how your brand can use it.
How Brands Can Leverage GA4
Google has provided several resources that marketers can use to get additional information on GA4. If your brand already has GA4 set up, good for you! If not, you can use Google’s migration resources to learn how to switch from Universal Analytics .
If your brand has yet to use any of Google’s analytic platforms in the past, Google also provides details on how to get started from scratch. Once you have GA4 set up, it’s essential to understand how to use it. Those familiar with Universal Analytics will notice that the GA4 platform looks quite different.
Below is an image of GA4 from Google, highlighting where to find your reports.
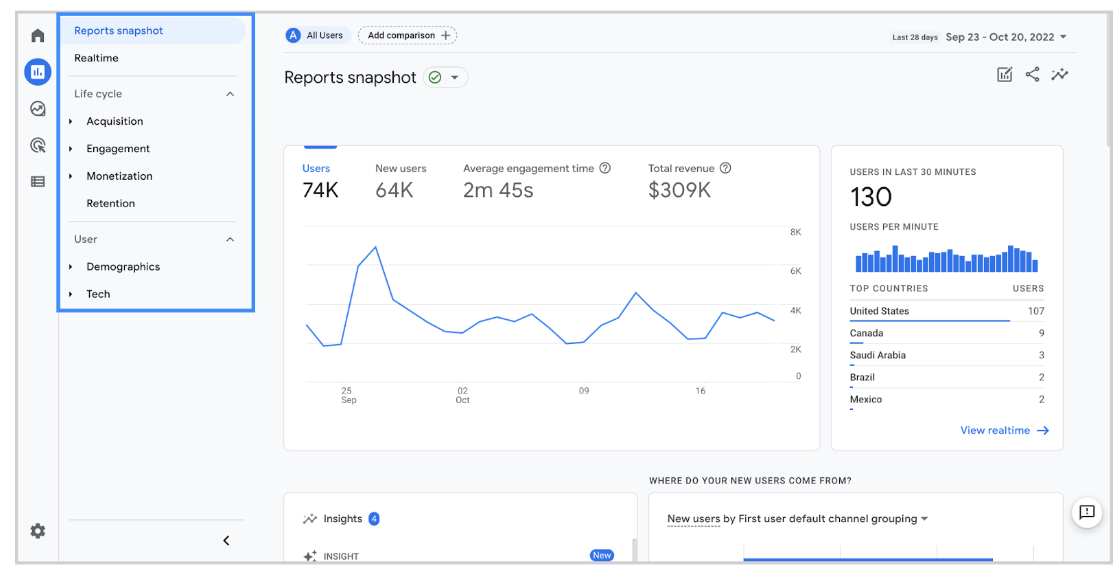
Google has also shared a resource highlighting the critical differences between Universal Analytics and GA4.
While you can find the full breakdown here, some of the key differences include:
- Users: GA4 has an extra metric to track users called active users. Active users are the number of distinct users who visited your website or application. They’ve had an “engaged session”, sessions longer than 10 seconds, or involves more than one page view or at least one conversion. This varies from new users — someone who has visited your site or launched your app for the first time.
- Pageviews: GA4 has removed unique pageviews and now only allows you to see the total number of pageviews. For instance, repeated views of a single page are counted. Google notes that pageviews in GA4 and unique pageviews in UA should be generally within a few percentage points of each other.
- Sessions: GA4 focuses on the session start. The difference in session count from Universal Analytics to GA4 can vary based on several factors, including geography, the use of UTMs, and filters.
As you can see, when you begin to report on GA4 versus Universal Analytics, you may see some distinct differences in your data; understand that this is normal and expected at first. Once you begin to leverage GA4, you’ll have an updated baseline of website performance.
Start Tracking Data Through GA4
Tracking how your brand performs online is a must. If you’re not already measuring how your local SEO efforts are performing, it’s time to start. That’s where GA4 comes in.
While understanding and leveraging GA4 is an essential first step, you can also find ways to improve your local search visibility by downloading our Top 10 Things You Should Be Doing in Local SEO Now guide.
Additionally, tools like SOCi Listings and SOCi Local Pages allow you to optimize your local SEO strategy and measure its success through the SOCi platform and GA4.





