Local Memo: Google Search Console Drops Page Experience Report, Adds Recommendations
Local Memo: SOCi Launches Consumer Behavior Index

Local Memo: SOCi Launches Consumer Behavior Index
In this week’s update, learn about SOCi’s Consumer Behavior Index; the impact of Google’s decision to shutter free GBP websites; Google’s improved fake review detection; the true nature of E-E-A-T; and what AI means for Google Maps.SOCi Launches Consumer Behavior Index
Today we’re launching a new report called the Consumer Behavior Index (CBI). The CBI is an extensive survey of more than 1,000 U.S. consumers, delving into behaviors and preferences related to these themes:- Using search and social platforms to find and discover local businesses
- The importance of peer feedback in local buying decisions
- Online interactions between consumers and local businesses
- The use of AI in local marketing
Over 20 Million Businesses May Be Losing Their Google Websites
We’ve mentioned in this space that Google has announced plans to sunset the free website builder that has been a part of Google Business Profiles for several years. Websites will begin redirecting to business profiles on March 1 and will shut down completely on June 10. As Search Engine Land points out, the impact of a lost website may extend to any ad campaigns that make use of the site as a landing page. For the most part, multi-location brands will not be impacted by this change, since most utilize local landing pages on corporate domains or other website solutions independent of Google. But some franchise businesses are seeing notices sent to their linked email accounts, alerting them to stray franchisees who may still be utilizing a free Google website. In all, some estimates indicate that more than 20 million free websites will be shut down.Google Improves Fake Review Detection by 45%
Google is reporting that a new machine learning algorithm improved the detection of fake local reviews by 45% in 2023, along with other improvements. Users upload 20 million contributions to Google local profiles every day. Google says it removed 5 million fake review attempts from a single source over a few weeks; some 170 million reviews that violated Google policies were removed during the course of the year. In all, Google cites about 200 million thwarted policy violations in 2023; this would suggest that approximately 3% of user contributions are caught and rejected by Google. It’s unknown how many violations are undetected.If E-E-A-T Isn’t a Ranking Signal, What Is It?
Google has issued clarifications in the past, and did so again the other day, about the nature of Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, commonly called E-E-A-T. Specifically, Google says E-E-A-T is not a ranking signal, system, or factor. So what, then, is E-E-A-T? Ryan Jones tells us that the concept originated in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines, the document that tells human website evaluators what they should look for when judging the quality of online content. Though evaluator ratings influence the creation and refinement of ranking signals, they do not impact ranking directly. For this reason, attempts to reverse engineer E-E-A-T by claiming, say, that having author bios and profiles on content pages establishes expertise, are misguided. For one thing, any specific tactics can easily be gamed with AI. In actuality, Google’s ranking methods are likely far more complex, taking into account aggregate data from very large numbers of users and websites. Rather than being a code SEOs can crack, E-E-A-T should be thought of, Jones says, as a guide to the kind of content that appeals to humans and that, very generally, Google will favor with algorithms that attempt to deliver satisfying results.What AI Means for Google Maps
Mike Blumenthal has a hands-on review of the new AI features in Google Maps, which he describes as SGE “bolted into” the navigation app. The new AI features are available only to certain Local Guides; the invite Blumenthal received asks him to try out the new features and provide feedback by clicking thumbs-up and thumbs-down buttons. Describing the user experience as “a little slow and verbose,” Blumenthal shares the example of a search for outdoor activities in Allegany, NY, noting that the activities suggested by Maps are not bad but fail to account for weather and other contextual factors that Google could be tapping into. Blumenthal also finds examples of hallucination, where a search for restaurants under $50 per person returns results that do not meet that criteria.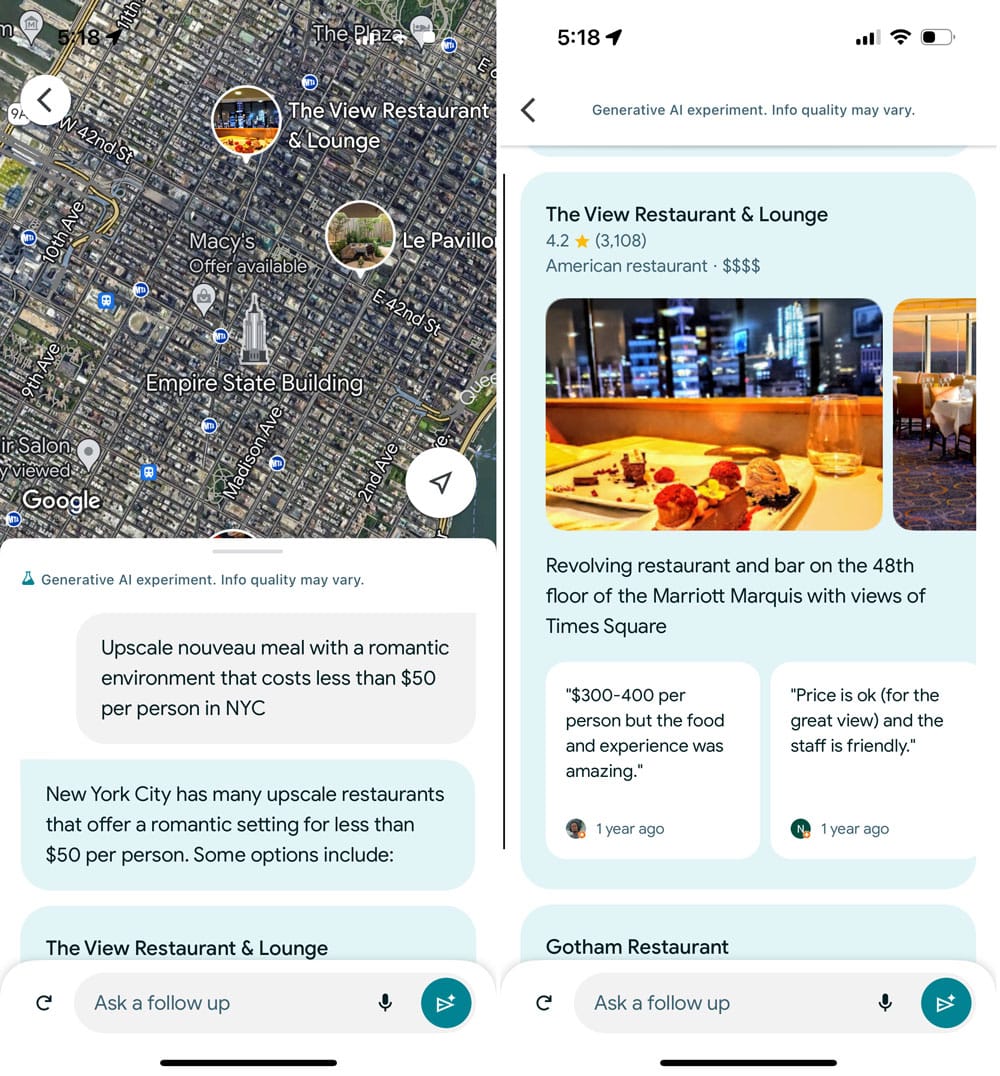
A search for romantic restaurants under $50 per person by Mike Blumenthal
Subscribe to Local Memo!
Signup to receive Local memo updates and the latest on localized marketing, delivered weekly to your inbox.







