The Basic Components and Branches of AI
The Basic Components and Branches of Artificial Intelligence
Advancements and interest in artificial intelligence (AI) have increased dramatically over the past several years. For instance, see the interest over time in Google Trends for users searching the term “AI” over the past two years.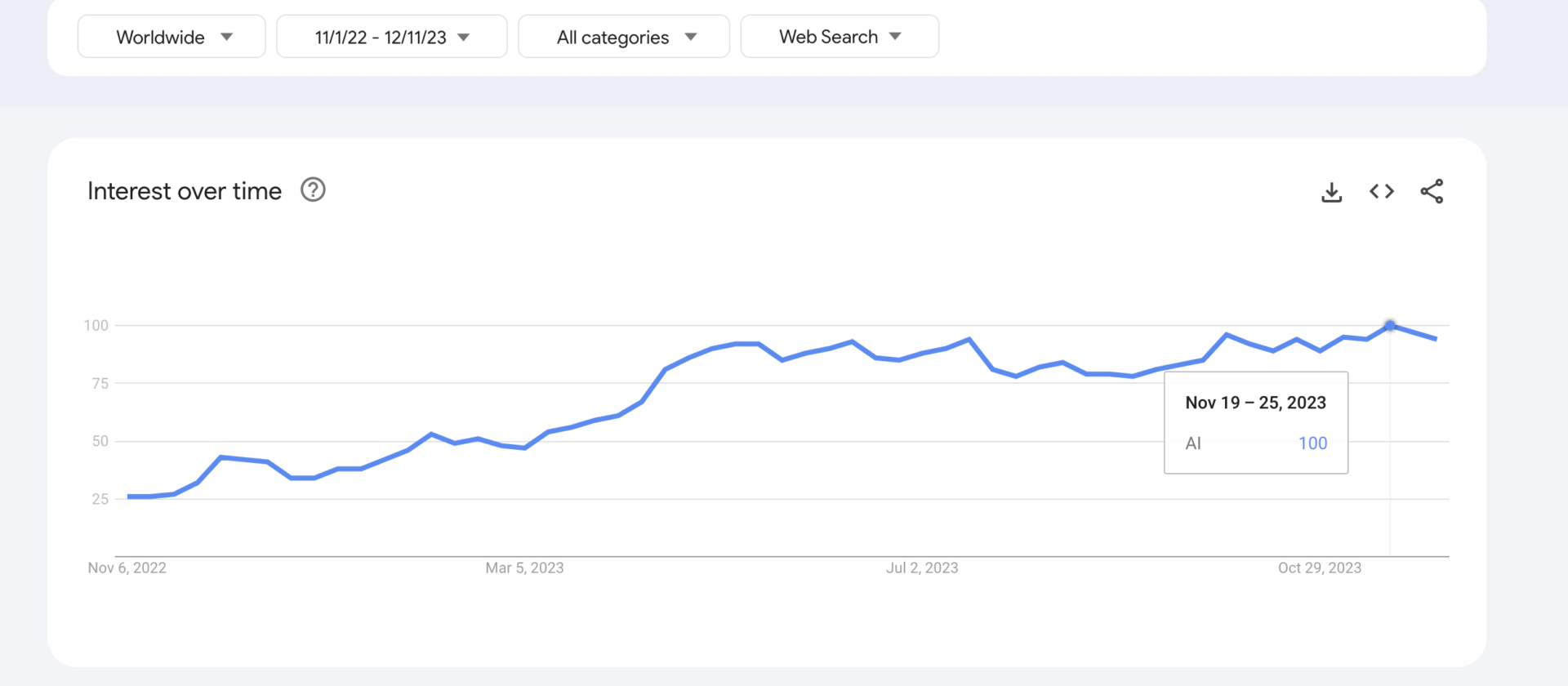
The Basic Components of AI
Before we jump into the different components of AI, let’s first define what artificial intelligence is. AI is a machine’s ability to perceive, synthesize, and infer information and then perform cognitive functions often associated with the human mind. Now, onto what engineers and scientists have developed to create the AI that we know today.1. Learning
Learning is a crucial component of AI as it enables AI systems to learn from data and improve performance without being explicitly programmed by a human. AI technology learns by labeling data, discovering patterns within the data, and reinforcing this learning via feedback, often in the form of rewards or punishments. Punishments are negative values associated with undesirable outcomes or actions. Example: Voice recognition systems like Siri or Alexa learn correct grammar and the skeleton of a language.2. Reasoning and Decision Making
The second major component of AI is reasoning and decision-making. AI systems can use logical rules, probabilistic models, and algorithms to draw conclusions and make inferred decisions. When faced with problems or issues, AI models should use reasoning to generate consistent results. Example: A writing assistant, like Grammarly, knows when or when not to add commas and other punctuation marks.3. Problem Solving
Problem solving in AI is similar to reasoning and decision making. AI systems take in data, manipulate it and apply it to create a solution that solves a specific problem. Example: A chess game understands its opponent's moves and then decides to make the best decision based on the game's rules and predicting future moves and outcomes.4. Perception
The fourth and final component of AI is perception. Perception refers to AI utilizing different real or artificial sense organs. The AI system can take in data and perceive suggested objects, and understand its physical relationship (e.gl, distance) to said objects. Perception often involves image recognition, object detection, image segmentation, and video analysis. Example: Self-driving cars gather visual data to recognize roads, lanes, and obstacles and then map these objects. See the example below of a Tesla 3’s navigational map.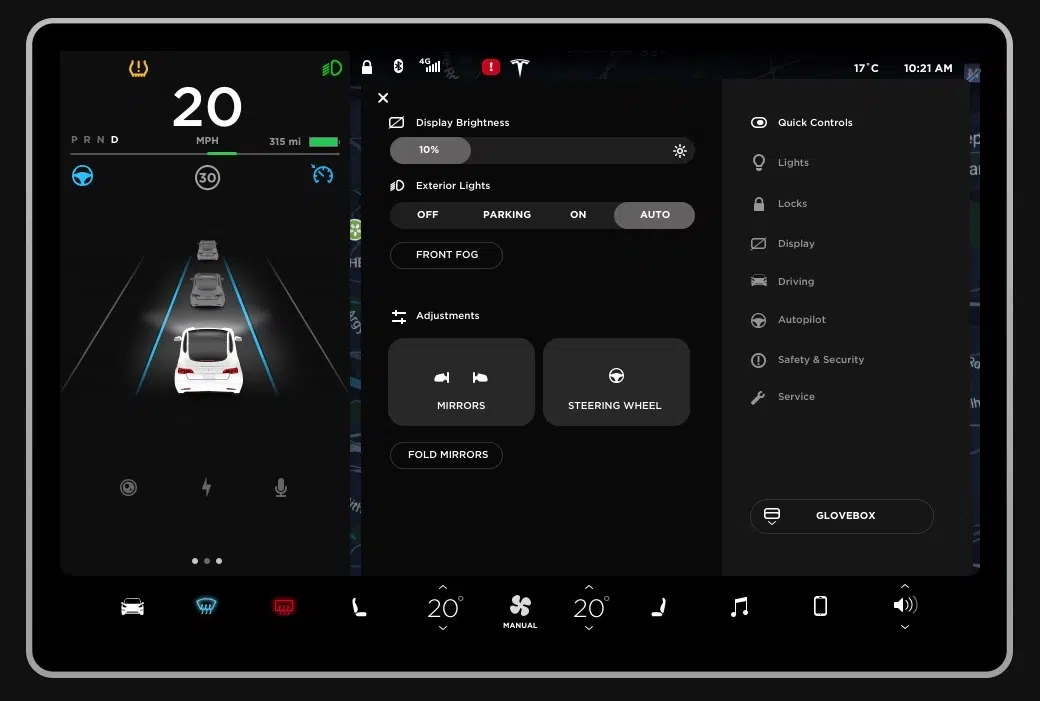
Courtesy of TechCrunch